Research activity
1. Unsupervised techniques for artificial intelligence
2. Analysis of biomedical images
3. Industrial and environmental informatics
4. Intrusion detection systtems
5. Biometric systems
The innovative techniques have been successfuly applied for signal and image processing in different application scenarios. In particular, the proposed methods include innovative, intelligent, and unsupervised algorithms based on Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks for processing palmprint images, for the high-accuracy recognition of individuals in security applications, and for processing histopathological images. The proposed techniques also include innovative and unsupervised artificial intelligence algorithms based on Generative Adversarial Networks and Explainable Artificial Intelligence for interpreting the aging process in face images. The research also focused on designing and realizing innovative and unsupervised methods based on Autoencoders and Explainable Artificial Intelligence to extract highly-discriminant and interpretable representations from general purpose images, enabling a classification of the samples with high accuracy, at the same guaranteeing a low dimensionality of the feature space.
2. Analysis of biomedical images
3. Industrial and environmental informatics
4. Intrusion detection systtems
5. Biometric systems
1. Unsupervised techniques for artificial intelligence
The research activities focused on the design and realization of innovative artificial intelligence techniques based on unsupervised learning, with the purpose of processing information without the need to associate each sample to its corresponding ground truth, therefore removing an important constraint that typically reduces the amount of usable data. The introduction of innovative and unsupervised techniques enabled the possibility to process large quantities of data using adaptive algorithms, with limited operational constraints, at the same time maintaining a high accuracy in the results. In particular, recent advances in the field of unsupervised generative models for data analysis and representation learning have been studied and analyzed. Moreover, the research activities resulted in the realization of methods for the adaptive, intelligent, and unsupervised extraction of highly-discriminant data representations with a limited feature dimensionality, for learning models using the inner data structure and not the ground truth, and for interpreting the data transformation process, with the purpose of simulating heterogeneous acquisition conditions.The innovative techniques have been successfuly applied for signal and image processing in different application scenarios. In particular, the proposed methods include innovative, intelligent, and unsupervised algorithms based on Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks for processing palmprint images, for the high-accuracy recognition of individuals in security applications, and for processing histopathological images. The proposed techniques also include innovative and unsupervised artificial intelligence algorithms based on Generative Adversarial Networks and Explainable Artificial Intelligence for interpreting the aging process in face images. The research also focused on designing and realizing innovative and unsupervised methods based on Autoencoders and Explainable Artificial Intelligence to extract highly-discriminant and interpretable representations from general purpose images, enabling a classification of the samples with high accuracy, at the same guaranteeing a low dimensionality of the feature space.
2. Analysis of biomedical images
The research activities regarded the design and realization of innovative methologies and software algorithms based on multidimensional signal processing and artificial intelligence techniques for the introduction of automated and adaptive biomedical systems. The proposed methods enabled to realize high-accuracy medical decision support systems, able to classify medical images captured with low-cost sensors and that can be used even by non-expert personell. In particular, the research focused in the areas of histopathological images, radiographic images, and images captured using mobile devices.- Histopathological images
The research activities focused on the design and realization of original methods based on Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks, Explainable Artificial Intelligence, and transfer learning for the high-accuracy classification of tumoral cells affected by Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, by considering low-dimensionality image databases of white blood cells and preprocessing techniques that enable Deep Learning models to process Whole Slide Images for the detection. The research also considered the design and realization of innovative methods based on transfer learning using heterogeneous databases of histopathological images, by experimentally evaluating how much knowledge can be shared among databases to increase the accuracy of Convolutional Neural Networks for tumor detection. - Radiographic images
The research focused on the design and realization of innovative methods based on Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks, Reinforcement Learning, and semantic segmentation for the analysis and classification of X-ray chest scans, with the purpose of detecting the presence of COVID-19 using a fast and scarcely intrusive procedure. - Images captured using mobile devices
The research focused on the design and realization of original algorithms based on image processing and pattern recognition for the analysis of fecal images captured using mobile devices, with the purpose of detecting the presence of biliary atresia with a scarcely intrusive approach, that can be used even by non-expert personnel.
3. Industrial and environmental informatics
The research has regarded the design and realization of innovative analysis methodologies, original hardware systems, and novel software algorithms for the monitoring, prediction, measurement, and adaptive classification of features extracted from multi-dimensional signals in industrial and environmental applications. The proposed solutions enabled to obtain high-accuracy results using low-cost acquisition technologies able to work at high distances, reducing operational and environmental constraints and enabling a remote deployment and an increased ease of management. In particular, the research has been carried out in the industrial and environmental areas.-
Industrial informatics
Innovative algorithms and methods based on multidimensional signal processing, three-dimensional models, and computational intelligence techniques have been studied and realized for the quantitative and qualitative analysis of materials and industrial processes using signals and images captured at high distances. Specific algorithms and methods based on Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks, Generative Adversarial Networks, and Explainable Artificial Intelligence have been studied and realized for the analysis, generation, and detection of synthetic defects in industrial products, for monitoring the production process of strand boards with low environmental impact, and for the measurement of the volume of the objects captured using multiple view systems. The proposed methods have also been validated with the deployment of a prototype in a factory. Moreover, the research activities focused on the study and realization of innovative pattern recognition approaches based on signal and image processing and on artificial intelligence techniques, with a specific focus on autonomous driving applications. In this context, the research focused on original methods based on Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks for estimating the distance of objects in the scene without requiring additional sensors. Moreover, the research focused on methods based on Convolutional Neural Networks to analyze the driver's attention level, by considering semantic segmentation techniques applied on images captured by a vehicle-mounted camera and photoplethysmography-based approaches. Lastly, the research activities focused on realizing innovative Deep Learning-based methods for monitoring the health level of electrical and electronics components in new-generation electric cars. -
XAI for semantic segmentation in automotive

-
Deep Learning for driver attention assistance

-
3-D volume estimation using CCD cameras
-
Innovative poplar low-density structural panel (I-PAN)

-
Environmental informatics
Innovative algorithms and methods based on multidimensional signal processing, computational intelligence techniques, and simulation techniques have been studied and realized for environmental monitoring and prediction systems. In particular, the research has been focused on advanced methods for wildfire detection systems based on the analysis of frame sequences captured at high distances using low-quality cameras and on the prediction of renewable energy using only weather forecasts or the information of energy unbalance in smart grids. Privacy issues and solutions in environmental monitoring systems have also been considered.
4. Intrusion detection systems
Artificial intelligence-based methods have been designed and developed for the adaptive detection of intrusions from heterogeneous datasets containing network activity logs. The proposed techniques achieved high accuracy in distinguishing benign network traffic from malicious traffic, while also enabling the classification of different types of intrusions. In particular, adaptive sizing methods for neural architectures have been designed and implemented to match the complexity of each specific dataset, also in synergy with knowledge transfer techniques, thus improving compatibility across heterogeneous databases. Moreover, innovative methods in federated learning scenarios have been studied and realized to select the best data to use for training and to to detect attacks, with the purpose of increasing the accuracy and robustness of intrusion detection approaches.5. Biometric systems
In the field of biometric systems, the research activities have regarded the design and realization of innovative solutions consisting in original hardware systems, software algorithms, and biometric methodologies for recognizing individuals in security applications using physiological traits and soft biometric features. The proposed methods enabled to reduce operational constraints of traditional biometric systems and allow a high-accuracy recognition using less-constrained and high-usability acquisition procedures. In particular, the research focused on touchless and less-constrained biometric systems and on high-usability touch-based systems.- Touchless and less-constrained biometric systems
In this context, the activities have been focused on innovative touchless and less-constrained acquisition procedures with a high usability, on new methods for the encoding of signal and images with a high level of noise, and on original methods for the comparisons of identities. In particular, different biometric traits have been studied. - Touchless and less-constrained fingerprint recognition
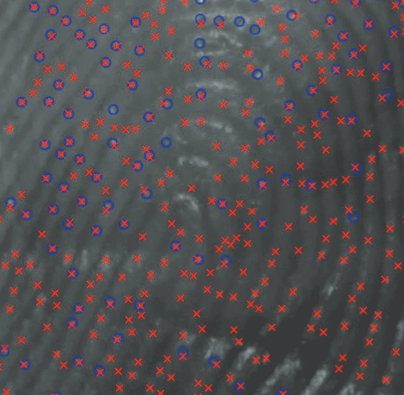
Innovative hardware systems, algorithms and biometric methods have been studied and realized for the recognition of fingerprints captured using less-constrained acquisition procedures, without the contact of the finger with the sensor. A particular focus has been given on the techniques for the processing of three-dimensional models for real-time identity comparisons and forensic applications. Methods for the extraction and analysis of features from samples captured using a single camera, mobile devices, as well as captured from heterogeneous sources, have been studied and realized. Methods for the quality estimation and the generation of synthetic of three-dimensional models have also been proposed. -
2-D touchless fingerprint recognition
-
3-D touchless fingerprint recognition
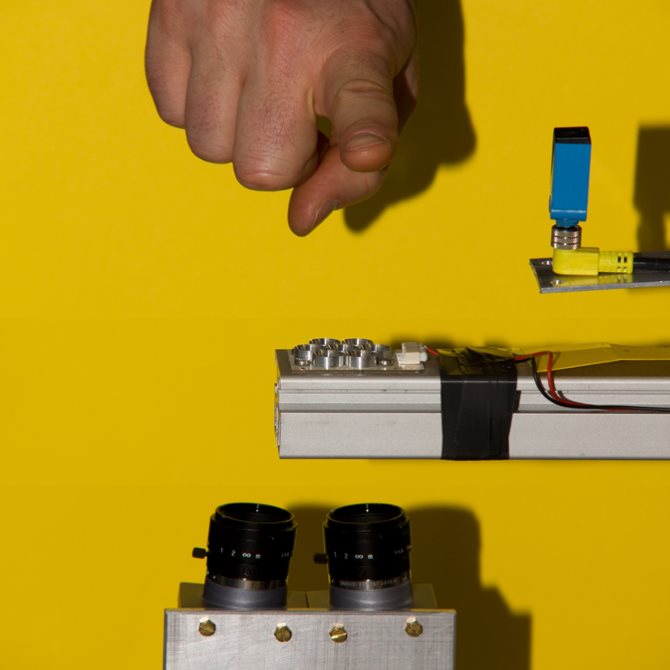
-
3-D models for ancient fingerprints

- Touchless and less-constrained palmprint recognition
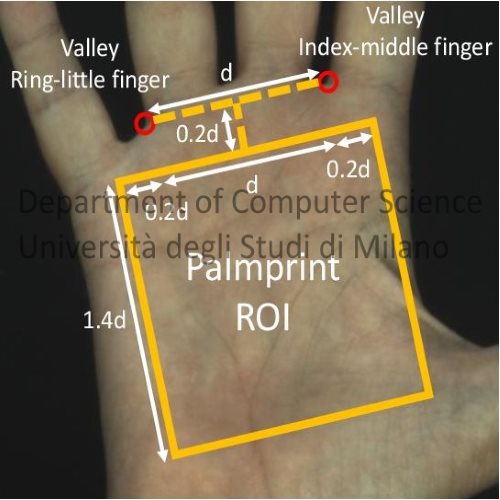
Innovative hardware systems, algorithms and biometric methods have been studied and realized for the recognition of palmprints captured using touchless and less-constrained acquisition procedures, without the contact of the hand with any surface. A specific focus has been given to novel Deep Learning-based techniques using original Convolutional Neural Networks, designed to extract highly-discriminative biometric features from palmprint images, trained using innovative unsupervised procedures. Original techniques based on Convolutional Neural Networks for the fusion of palmprint and finger texture features have also been proposed to increase the accuracy of the biometric recognition. The research also focused on new techniques for processing three-dimensional models and using pattern recognition methods for comparing samples captured with different positions and orientations. - Touchless and less-constrained recognition using soft biometric traits
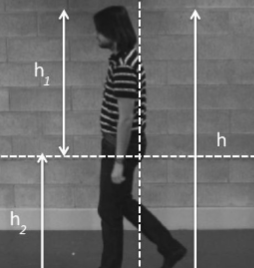
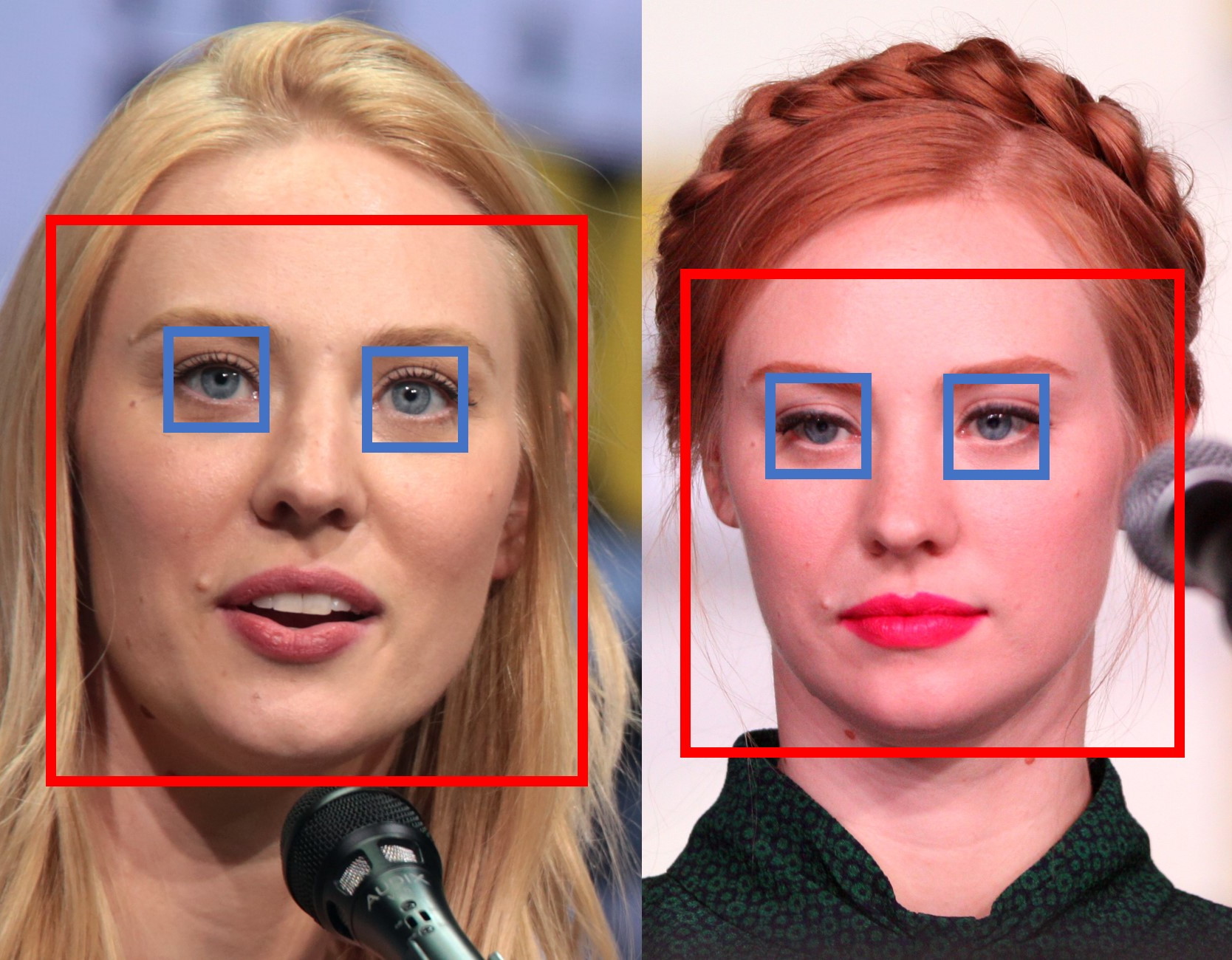
Innovative hardware systems and algorithms, based on multidimensional signal processing and computational intelligence techniques, have been studied and realized for the estimation of the weight of walking individuals in surveillance applications using touchless and un-obtrusive acquisition procedures. Multidimensional signal processing and computational intelligence techniques have also been used to estimate the age of the individuals using face images captured using un-obtrusive procedures. Explainable Artificial Intelligence techniques have been studied to analyze the learning process of Deep Learning-based methods that use Generative Adversarial Networks to synthetically age face images. - Less-constrained iris recognition
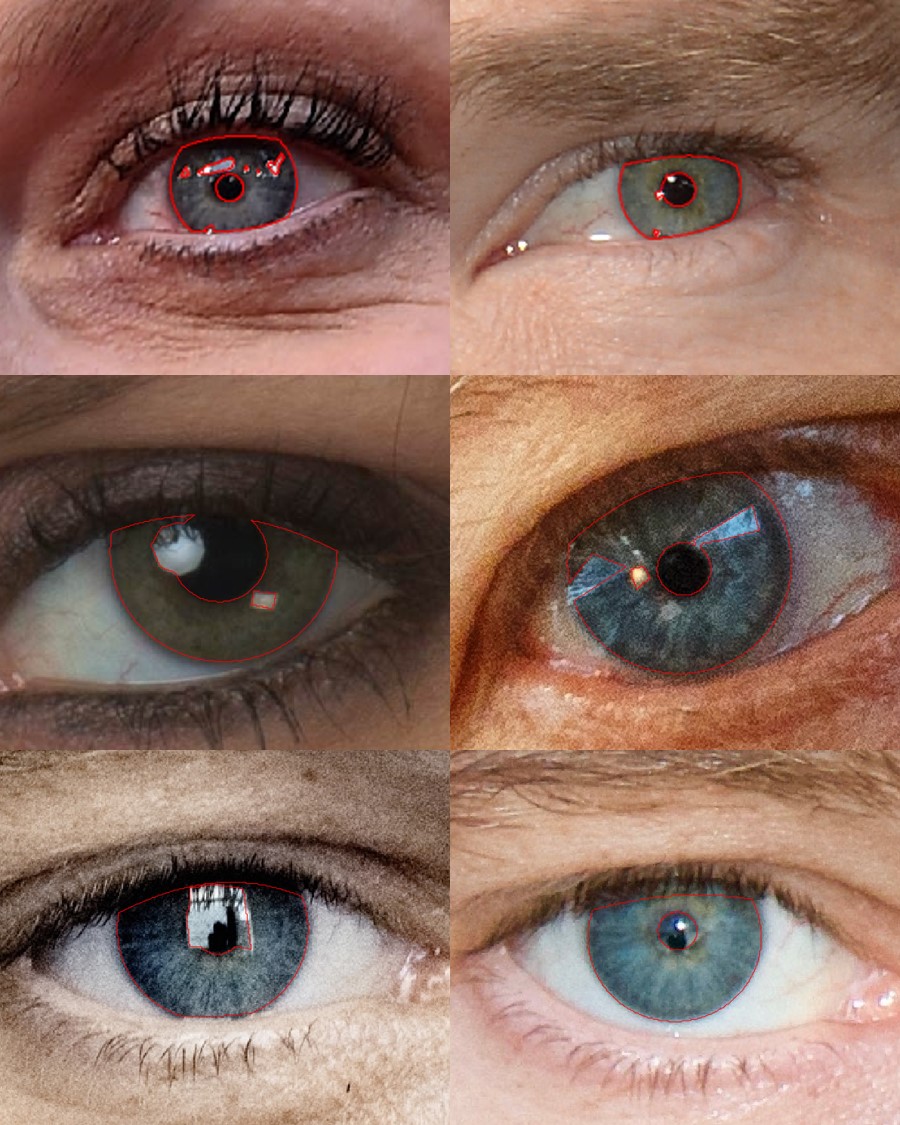
The research focused on studying the problems related to iris recognition and user tracking in security contexts, using public-domain images present on the internet and social media. To this purpose, the research activities also included the collection and publication of the first database, available to the public, of iris samples extracted from face images captured in less-constrained conditions and from images freely downloadable from the internet. The research acitivities included also the realization of an innovative methodology based on Generative Adversarial Networks to ensure the biometric anonymization of the iris in such images, at the same time maintaining a high visual realism of the obtained images. - Highly-usable touch-based biometric systems
Recent advances in biometric recognition for Automated Border Control (ABC) systems have been studied along with emerging technologies. Innovative algorithms and original biometric methods based on multidimensional signal processing and computational intelligence techniques have been studied and realized for a more accurate, fast, and highly-usable touch-based fingerprint recognition in new-generation Automated Border Control systems. In these applications, the research has focused on multimodal biometric systems, on techniques for the classification of acquisition problems affecting fingerprint images, and on methods for biometric score normalization.

 Google Scholar
Google Scholar Scopus
Scopus GitHub
GitHub DBLP
DBLP